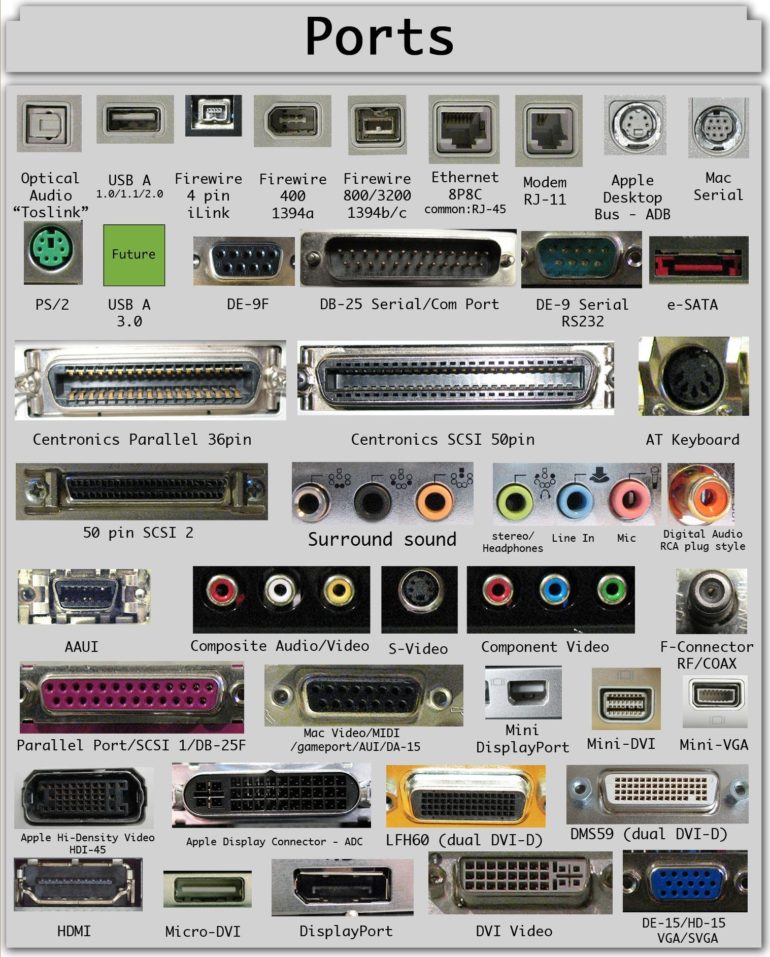
Today’s computers and mobile devices are available with a wide array of ports, from traditional USB to newfangled USB Type-C and Thunderbolt 3 ports. There are lots of different ports available for both desktop and laptop computers, each one with its own roles, different sizes.
Even if you’re familiar with the most common connectors, it can still be a challenge to figure out what wires or adapters you need in order to plug your device into a monitor, TV, network or peripheral. To help you find the right computer for your business, here are some of the most common types of ports and what they do.
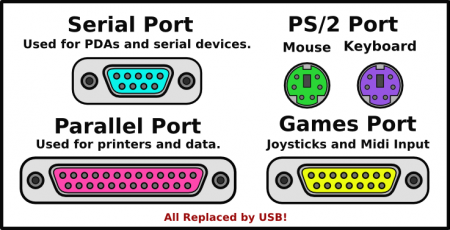
Serial ports
- Serial Port: A serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time. Once very commonly used for connecting an external modem or mouse to a PC, very few new computers will come with one unless specifically ordered that way.
- PS/2 Connector: Prior to 2010, the most commonly used connection for keyboards and mice to a PC compatible computer system. Its name comes from the IBM Personal System/2 series of personal computers, which replaced the even older 5-pin DIN connector for an AT keyboard. Some newer PCs may have a single combo PS/2 port that is half purple and half green. If present, these combo ports can accept either a PS/2 keyboard OR mouse. In any configuration, these ports carry a small electrical charge and the PC should be completely powered off before (un)plugging anything from/into them.
- Parallel Port: Sends several data signals simultaneously over several parallel channels (as opposed to the Serial Port). Once the most common interface for connecting a printer to a computer, these are also now non-existant in a modern PC.
- Game Port: The traditional connector for video game input devices on x86-based PCs.
- All of these ports have been replaced by USB (for which we all rejoice!).
Network ports
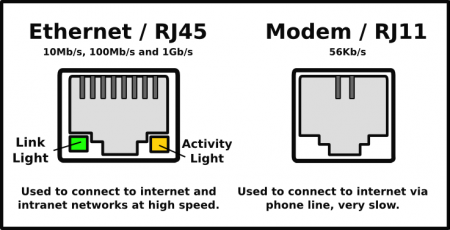

- Ethernet/RJ45: Most people consider this their network jack, internet connection or hardline. 10/100 (or Fast Ethernet, which replaced 10BASET/2/5) is slowly being replaced by 1000Mbit/s or Gigabit (GbE) ports. Technically, these ports are properly known as 8P8C (8 Position 8 Contact.) These ports are typically used to connect twisted pair (more commonly referred to as Cat5e) cable (or we could just say, “Plug in a network cable that gets you onto the internet”).
- Modem/RJ11: A physical interface often used for terminating telephone wires. Once standard issue with every desktop PC and laptop, new computers will often be without a modem/RJ-11 port unless specifically ordered that way.
Video ports
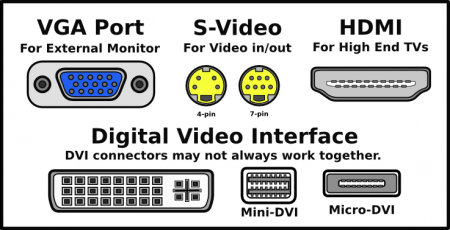

- VGA Port: Acronym for Video Graphic Array. The most common connection for external monitors, but not necessarily the most preferred as it carries an analog signal.
- S-Video: Separate Video (not Super Video) carries the video data as two separate signals, lumen (luminance) and chroma (colour).
- HDMI: High Definition Multimedia Interface is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. HDMI (currently at revision 1.4) is required for the complete transmission of audio streams exceeding 5.1 channels.
- DVI: Digital Video Interface is a video interface standard designed to provide very high visual quality on digital display devices such as flat panel LCD computer displays and digital projectors. Contrary to popular belief, it is possible to carry audio over a DVI connection provided both terminations support audio and they are connected via a 24+1 DVI (or DVI to HDMI) cable.
- Mini-DVI: This connector is used on Apple computers as a digital alternative to the Mini-VGA connector.
- Micro-DVI: This port is a video connection port used by some Apple MacBook Air laptop computers produced between January-October 2008.
Audio ports
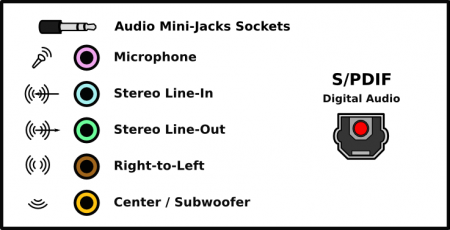

- Audio Mini-Jacks Sockets are self-explainable, you can find more comprehensive description of this interface here.
- S/PDIF: Or Sony/Phillips Digital Interconnect Format. More commonly referred to as an optical interface, and uses a TOSlink cable. The digital signal is limited to 5.1 Dolby Digital and/or DTS streams and cannot carry the additional audio streams found on Blu-Ray (in other words, 7.1 would be downmixed to 5.1 over S/PDIF).
Firewire ports
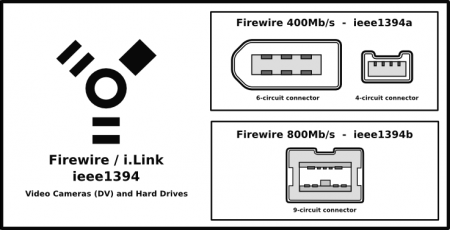

- Firewire 400MB/s: Can transfer data between devices at 100, 200, or 400 Mbit/s half-duplex data rates.
- Firewire 800Mb/s: Can transfer data at a rate of 786.432 Mbit/s full-duplex.
Power connectors
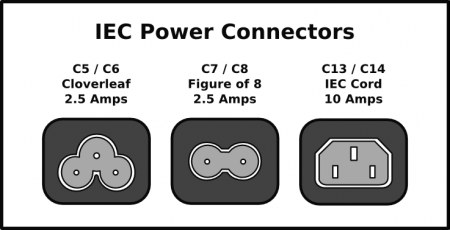

- C5 / C6: “Cloverleaf” or “Mickey Mouse” power connectors can be seen on the majority of laptop power supplies and portable projectors.
- C7 / C8: C7 is also sometimes called “Shotgun.” These connectors can be found on cassette recorders, battery/mains operated radios, some full size AV equipment, laptop computer power supplies, video game consoles.
- C13/C14: C14 is used as an inlet to attach the power cord to the power supply, as do many monitors, printers and other peripherals. While many older computers also provide a panel-mounting C13 outlet for powering the monitor.
USB ports
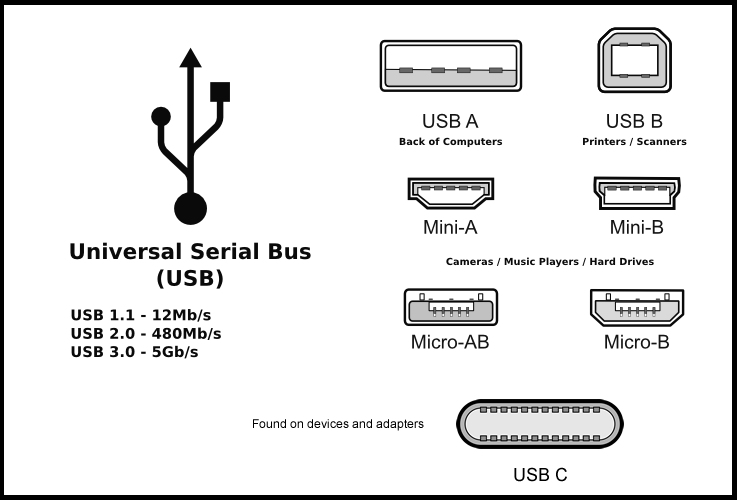

- USB-A: This kind of plug is most frequently seen on cables that are permanently attached to a device, such as one on a cable that connects a keyboard or mouse to the computer.
- USB-B: Typically plugs into an upstream receptacle on a device that uses a removable cable, e.g. a printer.
- USB-C: The 24-pin double-sided connector is slightly larger than the micro-B connector, with a USB-C port measuring 8.4 millimetres (0.33 in) by 2.6 millimetres (0.10 in). Two kinds (genders) of connectors exist, female (receptacle) and male (plug). Plugs are found on cables and adapters. Receptacles are found on devices and adapters.
- Micro-B: Micro plugs have a similar width as the Minis but approximately half the thickness. These enable integration into thinner portable devices.
- Micro-AB: This receptacle is capable of accepting either a Micro-A plug or a Micro-B plug
Other ports
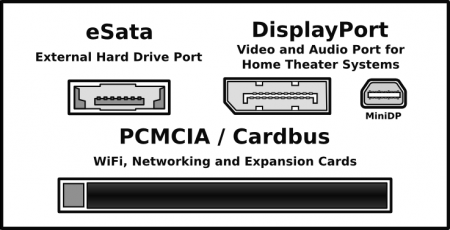

- eSata: External Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, standardised in 2004, provides a variant of SATA meant for external connectivity. Note that eSATA connectors are keyed differently than standard SATA, and that NO power is transferred over the eSATA bus or cables (in other words, you need a separate power source for your eSATA devices.)
- DisplayPort: Is a digital display interface standard put forth by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) since 2006. DisplayPort has been embraced by ATI/AMD and is required to run 3 or more monitors in an Eyefinity configuration.
- MiniDP: A miniaturised version of the standard DisplayPort.
- PCMCIA: Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (or, more commonly, PC Card) was used in a wide range of products (typically for laptops) such as WiFi, networking and flash memory. Other terms often associated with PCMCIA are Card Bus and its successor, ExpressCard; however, the PCMCIA Association was dissolved in 2009 and all Standards are now managed by the USB Implementers Forum.